Description
Summary
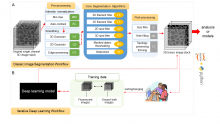
QuimP is software for tracking cellular shape changes and dynamic distributions of fluorescent reporters at the cell membrane. QuimP's unique selling point is the possibility to aggregate data from many cells in form of spatio-temporal maps of dynamic events, independently of cell size and shape. QuimP has been successfully applied to address a wide range of problems related to cell movement in many different cell types.
Introduction
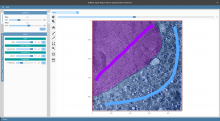
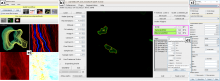
In transmembrane signalling the cell membrane plays a fundamental role in localising intracellular signalling components to specific sites of action, for example to reorganise the actomyosin cortex during cell polarisation and locomotion. The localisation of different components can be directly or indirectly visualised using fluorescence microscopy, for high-throughput screening commonly in 2D. A quantitative understanding demands segmentation and tracking of whole cells and fluorescence signals associated with the moving cell boundary, for example those associated with actin polymerisation at the cell front of locomoting cells. As regards segmentation, a wide range of methods can be used (threshold based, region growing, active contours or level sets) to obtain closed cell contours, which then are used to sample fluorescence adjacent to the cell edge in a straightforward manner. The most critical step however is cell edge tracking, which links points on contours at time t to corresponding points at t+1. Optical flow methods have been employed, but usually fail to meet the requirement that total fluorescence must not change. QuimP uses a method (ECMM, electrostatic contour migration method (Tyson et al., 2010) which has been shown to outperform traditional level set methods. ECMM minimises the sum of path lengths connecting all pairs of points, equivalent to minimising the energy required for cell deformation. The original segmentation based on an active contour method and outline tracking algorithms have been described in (Dormann et al., 2002; Tyson et al., 2010; Tyson et al., 2014).