Filament tracing
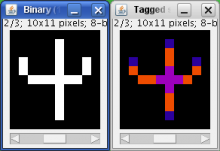
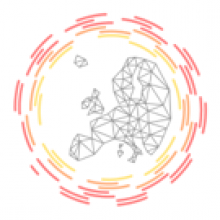
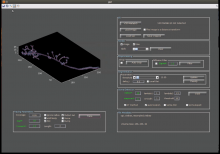
Filament tracing operations are image analysis operations in which there is an image of a filamentous structure (it may be a tree-like structure, a filament network or a agglomeration of single 'stick-like' filaments) as input and outputs data that represent the filament, most commonly a skeleton representation of the filaments and their diameters or surfaces.
Synonyms
Tubular structure extraction
biofilament tracing
Curvilinear structure reconstruction
Curvilinear structure detection
neuron image analysis
neuron reconstruction