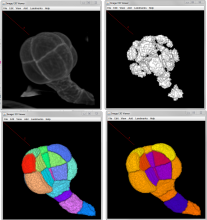
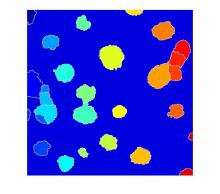
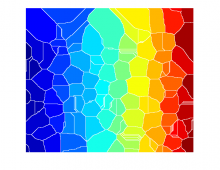
Watershed segmentation
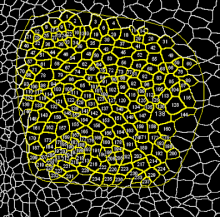
Watershed is the term that commonly refers to a mathematical morphology operation that treats a grayscale image as a topographic map and segments the image. The segmentation is performed by a succesive 'flooding' operation from minima in the image starting from different points and separates the image in different catchment basins.|Needs a comment about the relation between the Watershed and Region growing.
Synonyms
Watershed transformation
Watershed-based segmentation